I know Everyone is Thinking about Google showing 'Indexing Requested' instead of 'Indexed' in Webmaster Tools while Feching and Rendering your URL's
Run a fetch
- In the textbox, enter the path component of a URL on your site that you want Googlebot to fetch, relative to the site root. Leaving the textbox blank fetches the site root page. For example, if the current property is
http://example.com, a request forstores/indiana/1234.htmlwould fetchhttp://example.com/stores/indiana/1234.htmlFetch restrictions:- Fetched URLs are limited to the current site: for example, if the current Search Console property is to
http://example.comyou cannot fetch a URL fromhttps://example.comorhttp://m.example.com. - The fetch does not send any cookies, login information, or other state information.
- The fetch will not follow a redirect. If you fetch a page with a redirect, you will have to follow it manually as described in the "Redirected" fetch status description below.
- Fetched URLs are limited to the current site: for example, if the current Search Console property is to
- Optionally choose a type of Googlebot you wish to perform the fetch as. This affects the crawler making the fetch, and also the rendering for a Fetch and Render request. The following types are available:
- Desktop [Default] -
- For websites, uses the Googlebot crawler.
- For news, uses the Googlebot crawler (not Googlebot News).
- For images, uses the Googlebot Images crawler.
- For videos, uses the Googlebot Video crawler.
- For pages with AdSense code, uses Google AdSense crawler.
- For ad landing pages, uses Google AdsBot crawler.
- Mobile: Smartphone
- Current - Uses the current (but soon to be replaced) version of the Google Smartphone crawler.
- Upcoming - Uses the latest version of the Google Smartphone crawler.
- Desktop [Default] -
- Click either Fetch or Fetch and Render:
- Fetch: Fetches a specified URL in your site and displays the HTTP response. Does not request or run any associated resources (such as images or scripts) on the page. This is a relatively quick operation that you can use to check or debug suspected network connectivity or security issues with your site, and see the success or failure of the request.
- Fetch and render: Fetches a specified URL in your site, displays the HTTP response and also renders the page according to a specified platform (desktop or smartphone). This operation requests and runs all resources on the page (such as images and scripts). Use this to detect visual differences between how Googlebot sees your page and how a user sees your page.
- The request will be added to the fetch history table, with a "pending" status. When the request is complete, the row will show the success or failure of the request and some basic information. Click any non-failed fetch row in the table to get additional details about the request, including raw HTTP response headers and data, and (for Fetch and Render) a list of blocked resources and a view of the rendered page.
- If the request succeeded and is less than four hours old, you can tell Google to re-crawl and possibly re-index the fetched page, and optionally any pages that the fetched page links to.
You have a weekly quota of 500 fetches. When you are approaching your limit, you will see a notification on the page.
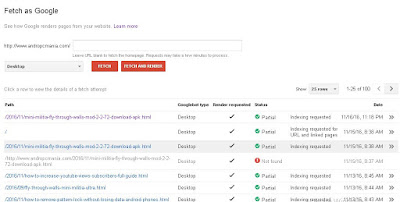
Request fetch status
The fetch history table on the main page shows the last 100 fetch requests. To see details for a completed fetch, click on the corresponding row in the fetch history table. The following request fetch statuses can be displayed:
- Complete: Google successfully contacted your site and crawled your page, and can get all resources referenced by the page. Click the table row to see more details about the fetch results.
- Partial: Google got a response from your site and fetched the URL, but could not reach all resources referenced by the page because they were blocked by robots.txt files. If this is a fetch only, do a fetch and render. Examine the rendered page to see if any significant resources were blocked that could prevent Google from properly analyzing the meaning of the page. If significant resources were blocked, unblock the resources on robots.txt files that you own. For resources blocked by robots.txt files that you don't own, reach out to the resource site owners and ask them to unblock those resources to Googlebot. See the list of resource fetch error descriptions.
- Redirected: The server responded with a redirect. The Fetch as Google tool does not follow redirects. Although the actual Google crawler follows redirects, the Fetch as Google tool will not. You must follow a redirect manually:
- If the redirect is to the same property, the tool displays a button that allows to quickly follow the redirect by populating the fetch box with the redirect URL.
- If the URL redirects to another property that you own, you can click "Follow" to autopopulate the URL box, then copy the URL, switch views to the new site, and then paste the URL into the fetch box.
- Specific error type... Any of the resource type fetch errors can also apply to a fetch request for the entire page and can be shown in the status column. For example: Not found or Unreachable.
Resource fetch errors
If the fetch request status is Partial, click the request to open the request details page. The table on the page will list any errors encountered. Typically the errors are due to blocked resources on the page. The following resource errors can occur in a fetch request:
Fetch as Google showing 'Indexing Requested' instead of 'Indexed'
This is not a problem or any type of error For your Website/ Blog . This is Just a Message Shown on Webmaster Tools and when You Fetch Your Url it Will Just Display Some Message
Note: The page will be considered for indexing only if it meets our quality guidelines and avoids the use of noindex directives
Aa Webmaster Tool is Upgraded This is the new Feature but there is no Post or Article by WebmasterTools on this "Index Requested " so Lets hope Google Upadates About it Soon !!!!!!!
If You Know Some Thing About it Update Below In comments ! Thank you !



No comments:
Post a Comment